 Three-fourths of patients with Alzheimer’s disease or frontal-lobe degeneration had MRI-detected biomarker levels that correlated with the diagnoses, suggesting MRI has potential as a screening tool for the conditions, investigators reported.
Three-fourths of patients with Alzheimer’s disease or frontal-lobe degeneration had MRI-detected biomarker levels that correlated with the diagnoses, suggesting MRI has potential as a screening tool for the conditions, investigators reported.
MRI-predicted values for total tau and β-amyloid ratio (tt/Aβ) in gray matter correctly pinpointed the diagnosis in 75% of patients with genetically or neuropathologically confirmed diagnoses, according to Corey McMillan, PhD, of the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, and colleagues. Predicted values also had good correlation with actual tt/Aβ measured in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), they said.
The findings are consistent with previous in vivo and autopsy studies of CSF tt/Aβ, the group reported in the Jan. 8 issue of Neurology.
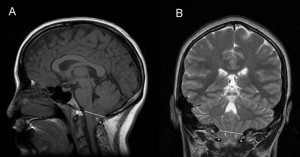
 For the very first times, surgeons at Johns Hopkins have used a brain-implanted pacemaker device to try to slow memory loss in a patient suffering from the early stages of Alzheimer’s. So far there’s only one patient with a memory-saving zapper, but a second is on the way along with about 40 others over the course of the next year, with the help of several other research institutes. After implantation, the pacemakers zap a part of the brain called the fornix with up to 130 blasts of electricity per second, all without disturbing the brain’s owner.
For the very first times, surgeons at Johns Hopkins have used a brain-implanted pacemaker device to try to slow memory loss in a patient suffering from the early stages of Alzheimer’s. So far there’s only one patient with a memory-saving zapper, but a second is on the way along with about 40 others over the course of the next year, with the help of several other research institutes. After implantation, the pacemakers zap a part of the brain called the fornix with up to 130 blasts of electricity per second, all without disturbing the brain’s owner. A mutation found in about one in 200 Icelanders older than 85 raised the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease threefold, researchers said.
A mutation found in about one in 200 Icelanders older than 85 raised the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease threefold, researchers said.